Permaculture companion plants for Yarrow
| Image | Name | Data | Description | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Apricot |
4-8
Perennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium
Deciduous
9.0
Trees
Adhesive, Dye, Gum, oil, Lumber, Espalier
true
Fruit, Seed
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prunus_armeniaca
Medium
Rosaceae
true
Oil, Gum
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Prunus armeniaca
China North-Central, China South-Central, Inner Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Kirgizstan, Kriti, Manchuria, Qinghai, Uzbekistan, Xinjiang
Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Bulgaria, California, Central European Rus, Colorado, Corse, Cyprus, East European Russia, East Himalaya, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Idaho, Illinois, Iowa, Iran, Italy, Kansas, Korea, Krym, Lebanon-Syria, Libya, Michigan, Missouri, Montana, Morocco, New Mexico, New South Wales, North Caucasus, Oregon, Pakistan, Pennsylvania, Portugal, Queensland, Romania, Sardegna, South Australia, South European Russi, Tadzhikistan, Transcaucasus, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Utah, Virginia, Washington, West Himalaya, Yugoslavia
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:729463-1
|
The apricot is a tree native to China and Central Asia. It typically grows to be about 20-30 feet tall and has a spreading, round canopy. The leaves are oval-shaped and about 2-4 inches long, with a serrated edge and a glossy green surface. The flowers are white or pink and have five petals. The fruit is a drupe, similar in appearance to a peach, with a smooth, orange skin and a fleshy interior. Apricots are known for their sweet flavor and are often used in jams, jellies, and other preserves. The fruit can also be eaten fresh or dried. The seed, or pit, of the apricot contains a small amount of cyanide and should not be eaten. Apricots prefer a warm, sunny climate and well-draining soil. They are sensitive to frost and can be damaged by cold temperatures. To successfully grow apricots, they should be planted in an area with full sun exposure and watered regularly. Apricots have a number of uses beyond their delicious fruit. The wood of the tree is often used for smoking meats, and the leaves can be used as a natural insecticide. In traditional medicine, apricot oil has been used to treat a variety of ailments. |
Show
Edit |

|
Anthriscus cerefolium |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chervil
true
Moist
Full sun, Partial sun/shade, Full shade
6-9
Garden chervil
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Apiaceae or umbelliferae
0.5
Echte kerbel
Leaves, Root
Biennial
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Anthriscus cerefolium
Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Austria, Baleares, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canary Is., Corse, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, East Aegean Is., Egypt, France, Germany, Greece, Gulf States, Hungary, India, Iran, Iraq, Italy, Kazakhstan, Kirgizstan, Kriti, Krym, Lebanon-Syria, Libya, Madeira, Morocco, Netherlands, North Caucasus, Oman, Pakistan, Palestine, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Sardegna, Saudi Arabia, Sicilia, Sinai, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Transcaucasus, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, West Himalaya, Xinjiang, Yugoslavia
Alabama, Argentina Northeast, Arizona, British Columbia, California, Chile Central, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Great Britain, Ireland, Japan, Korea, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Jersey, New South Wales, New York, New Zealand North, New Zealand South, North Carolina, Ohio, Ontario, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode I., Saskatchewan, South Australia, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tasmania, Tennessee, Texas, Victoria, Washington
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:40487-1
Condiment
Fragrance
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
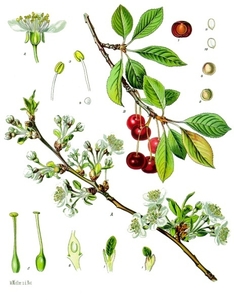
Sweet cherry |
3-7
Perennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Deciduous
18.0
Trees
Dye, Gum, Tannin, Lumber, Espalier
true
Fruit, Seed
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prunus_avium
Fast
Sweet cherry
Rosaceae
Süßkirsche
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Prunus avium
183
Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Corse, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, France, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Hungary, Iran, Ireland, Italy, Krym, Libya, Morocco, Netherlands, North Caucasus, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Sardegna, Sicilia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Transcaucasus, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Ukraine, Yugoslavia
Arizona, Baleares, Baltic States, British Columbia, California, Central European Rus, Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia, East European Russia, East Himalaya, Finland, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Kazakhstan, Kentucky, Korea, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New South Wales, New York, New Zealand North, New Zealand South, North Carolina, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Ontario, Oregon, Pakistan, Pennsylvania, Rhode I., South Australia, South Carolina, South European Russi, Tadzhikistan, Tennessee, Turkmenistan, Utah, Victoria, Virginia, Washington, West Himalaya, West Virginia, Wyoming
3
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:30093848-2
Gum
|
The sweet cherry, Prunus avium, is a fruit-bearing tree that is native to Europe, western Asia, and northern Africa. It typically grows to a height of 15-30 feet, with a spread of 20-25 feet, and has a rounded crown. The leaves are oblong-shaped, with serrated edges and a glossy dark green color. The flowers are white or pale pink, with five petals, and appear in clusters in the spring before the leaves. The fruit, which is the sweet cherry, is a small, round drupe, with a smooth, dark red or black skin and a juicy, sweet flesh. In terms of growing conditions, the sweet cherry prefers well-drained, fertile soil and full sun exposure. It can be grown in a variety of climates, but may require protection from frost in harsh climates. To cultivate the sweet cherry successfully, a grower may need to prune the tree to maintain its shape, provide adequate water and fertilizer, and protect the tree from pests and diseases. The sweet cherry is edible and can be eaten fresh or used in a variety of culinary dishes. The fruit can be stored in the refrigerator for a few days or preserved by freezing or canning. The sweet cherry is also valued for its medicinal properties, as the fruit and leaves have been used in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments. In terms of its value for wildlife, the sweet cherry provides food for a variety of animals, including birds, squirrels, and other small mammals. It also provides shelter and habitat for these animals. |
Show
Edit |
|
Sour cherry |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prunus_cerasus
true
Moist
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
3-7
Trees
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Rosaceae
6.0
Sauerkirsche
Oil, Gum, Tea
Fruit, Seed
Adhesive, Dye, Gum, Hedgerow, oil, Lumber
Perennial
Deciduous
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Prunus cerasus
North Caucasus
Afghanistan, Alaska, Argentina South, Austria, Baltic States, Belgium, British Columbia, Bulgaria, California, Central European Rus, Connecticut, Czechoslovakia, Delaware, District of Columbia, East European Russia, East Himalaya, France, Georgia, Germany, Great Britain, Hungary, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Iran, Ireland, Irkutsk, Italy, Kansas, Kazakhstan, Kentucky, Korea, Madeira, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New South Wales, New York, New Zealand North, New Zealand South, North Carolina, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Ontario, Oregon, Pakistan, Pennsylvania, Poland, Portugal, Prince Edward I., Québec, Rhode I., Sardegna, Sicilia, South European Russi, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Transcaucasus, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Himalaya, West Siberia, West Virginia, Xinjiang, Yugoslavia
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:729574-1
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
Peach |
5-9
Perennial
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
6
Trees
true
Flowers, Fruit, Seed
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peach
Fast
Flowering peach, ornamental peach, common peach
Rosaceae
Pfirsich, bergpfirsich, tellerpfirsich, saturnpfirsich, weinbergpfirsich
Oil, Gum, Tea
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Prunus persica
China North-Central
Afghanistan, Alabama, Argentina Northwest, Arizona, Arkansas, Assam, Baleares, Bulgaria, California, Cape Verde, China South-Central, China Southeast, Colorado, Connecticut, Corse, Cyprus, Delaware, District of Columbia, East European Russia, East Himalaya, Ecuador, El Salvador, Ethiopia, Florida, France, Free State, Georgia, Greece, Hungary, Idaho, Illinois, India, Indiana, Iowa, Iran, Italy, Japan, Kansas, Kazakhstan, Kentucky, Kenya, Kirgizstan, Korea, Kriti, Krym, KwaZulu-Natal, Laos, Libya, Louisiana, Maine, Marianas, Maryland, Massachusetts, Mauritius, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, New Jersey, New Mexico, New South Wales, New York, New Zealand North, North Carolina, North Caucasus, Northern Provinces, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Oklahoma, Ontario, Oregon, Pakistan, Pennsylvania, Portugal, Queensland, Rhode I., Rodrigues, Romania, Réunion, Sardegna, South Australia, South Carolina, South European Russi, St.Helena, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Tennessee, Texas, Transcaucasus, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Utah, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, Virginia, West Himalaya, West Virginia, Wisconsin
3
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:1212858-2
Adhesive, Cleanser, Dye, Gum, oil, Espalier
|
The peach, scientifically known as Prunus persica, is a deciduous tree native to northwest China. It typically grows to be about 10-30 feet tall, with a short trunk and a rounded crown. The leaves are oval-shaped, with serrated edges and a glossy, dark green color. The flowers are pink and white, with five petals each. Peaches are known for their fuzzy, peach-colored skin and juicy, sweet flesh. They can be eaten fresh, canned, or cooked into dishes such as pies and cobblers. The edible parts of the peach include the flesh and the seed, which contains a small kernel that can be ground into flour. Peaches can be stored after harvest by keeping them in a cool, dry place. Peaches prefer well-draining, loamy soil and full sun. They can be grown in a variety of climates, but do best in warm, temperate regions. To cultivate peaches successfully, growers may need to provide support for the trees, prune them regularly, and protect them from pests and diseases. Peaches are generally winter hardy, but can be damaged by frost. In addition to being eaten fresh, peaches have a variety of uses. The flowers can be used in herbal teas, and the leaves can be used to make a yellow dye. The wood of the tree can be used for smoking meat, and the kernels can be used to make oil. Peaches are also a valuable food source for wildlife, attracting birds, squirrels, and other animals. |
Show
Edit |

|
Nectarine |
4-8
Perennial
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Deciduous
6.0
Trees
Adhesive, Cleanser, Dye, Gum, oil, Espalier
true
Flowers, Fruit, Seed
Rosaceae
Nektarine
Oil, Gum, Tea
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Prunus persica nucipersica
Nectarine
Nektarin
3
|
Nectarine (Prunus persica nucipersica) is a plant that is a type of stone fruit. It is native to China and is closely related to the peach. Nectarines are similar in appearance to peaches, but have smooth skin rather than fuzzy skin. They can range in size from small to large and are typically round or oval in shape. Nectarines have green or red leaves and white or pink flowers. The stems of the plant are generally thin and have thorns. Nectarines can grow to be quite large, reaching heights of up to 8 meters. They grow best in warm, sunny climates and well-drained soil. To cultivate nectarines successfully, a grower will need to provide the plant with plenty of sunlight and water. They may also need to prune the plant to maintain its shape and encourage new growth. Nectarines are edible and the fruit can be eaten fresh or cooked. The edible parts of the fruit can be stored in a cool, dry place after harvest. Nectarines have several uses. In addition to being eaten fresh or cooked, they can also be used to make jams, jellies, and other preserves. They can also be dried and used as a snack. In addition to their culinary uses, nectarines have been used medicinally for their high vitamin and mineral content. They are also valued for their ability to attract wildlife, such as birds and bees, to the garden. |
Show
Edit |

|
Apple |
3-8
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Deciduous
10.0
9
Perennial
Trees
Animal feed, Attracts insects, Hedgerow
True
Fruit
Oil
Appel
Æble
Rosaceae
Malus
Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, Kirgizstan, Pakistan, Tadzhikistan, Uzbekistan, Xinjiang
Alabama, Alaska, Albania, Argentina Northeast, Argentina South, Arkansas, Azores, Baleares, Baltic States, Belarus, Belgium, British Columbia, Bulgaria, California, Central European Rus, Colorado, Connecticut, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, Delaware, Denmark, District of Columbia, East European Russia, East Himalaya, Ecuador, Falkland Is., Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Hungary, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Iraq, Ireland, Italy, Kansas, Kentucky, Korea, Krym, Louisiana, Madeira, Maine, Manitoba, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nepal, Netherlands, Nevada, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New South Wales, New York, Newfoundland, North Carolina, North Caucasus, North Dakota, Norway, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Ontario, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Poland, Prince Edward I., Québec, Rhode I., Romania, South Carolina, South European Russi, Spain, Sweden, Tasmania, Tennessee, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Utah, Vermont, Victoria, Virginia, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming, Yugoslavia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apple
https://pfaf.org/user/plant.aspx?LatinName=Malus+domestica
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:726282-1
Apfel
|
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (Malus domestica). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus Malus. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, Malus sieversii, is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonists. Apples have religious and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek, and European Christian tradition. Apples grown from seed tend to be very different from those of their parents, and the resultant fruit frequently lacks desired characteristics. Generally, apple cultivars are propagated by clonal grafting onto rootstocks. Apple trees grown without rootstocks tend to be larger and much slower to fruit after planting. Rootstocks are used to control the speed of growth and the size of the resulting tree, allowing for easier harvesting. There are more than 7,500 known cultivars of apples. Different cultivars are bred for various tastes and uses, including cooking, eating raw, and cider production. Trees and fruit are prone to a number of fungal, bacterial, and pest problems, which can be controlled by a number of organic and non-organic means. In 2010, the fruit's genome was sequenced as part of research on disease control and selective breeding in apple production. Worldwide production of apples in 2018 was 86 million tonnes, with China accounting for nearly half of the total. From [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apple) |
Show
Edit |

|
Common Grape Vine |
6-10
Perennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Dry, Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Deciduous
15-32m
Vines
True
Flowers, Fruit, Leaves, Seed
Seed - direct sow, Cuttings
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitis_vinifera
Fast
Wine grape, Purpleleaf grape, Common grape, Angur, Diva loza, Grozde yagorida, Tumpeang ba'y chu, Uva, Vid, Vigne, Vino, Weinrebe, Aanab, Ainab, Aitoviiniköynnös, Lehti, Angoor, Angur, Blad från vinranka, Bortermo szolo levél, Cognac oil, Common grape vine, Dakh, Darakh, Drakh, Draksa, Draksh, Draksha, Draksha kottai, Draksha pondu, Drakshai, Drakya, Dry grapes, Drak?a (fruit), European grape, Feuille de vigne rouge, Folha de videira, Frunze de vita-de-vie, Gostani, Gostoni, Grape, Grape seeds oligomeric proanthocyanidins, Grape vine, Grapevine, Grapevine leaf, Kashmish, Kishmish, Kottai drakshai, Lambrusca, Lambrusque, Lie de vin, List vinica, List vinske trte, Lisc winorosli wlasciwej, Maneka, Maweez munaqqa, Maweezak kohi, Munaca, Munaqqa, Munkka, Munthringya, M?dvika, Parra, Raisins, Rote weinrebenblätter, Rød vinranke, Blad, Tikruju vynmedžiu lapai, Vid, Hoja de, Vigne, Vigne rouge, Vigne vinifère, Viinapuu lehed, Vinblad, Vine, Vinho, Vino, Vite, Foglia, Vitis vinifera, Flos, Vitis viniferae folium, Vínviðarlauf, Weinrebe, Werqa tad-dielja, Wijnstokblad, Wine, Wine grape, Zabeeb-ul-jabal, Cervený list vinné révy, Ista vinkoka lapas
Vitaceae
Weintraube
Oil
https://pfaf.org/user/plant.aspx?latinname=Vitis+Vinifera
Southern Europe, Central Europe, Southwestern asia , Albania, Austria, Bulgaria, Corse, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iran, Iraq, Italy, Kirgizstan, Krym, Lebanon-Syria, North Caucasus, Palestine, Romania, Sardegna, Sicilia, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Transcaucasus, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Yugoslavia
4.3-8.6
Tap
0.6-6m
8feet
6 weeks
20°c (69°f)
12 months
False
Druif
Vindrue
Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Argentina Northeast, Azores, Baleares, Bangladesh, Belgium, British Columbia, California, Canary Is., Cape Verde, Caroline Is., Chad, China North-Central, China South-Central, China Southeast, East Aegean Is., East European Russia, East Himalaya, Easter Is., Ecuador, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gulf of Guinea Is., Idaho, India, Kazakhstan, Korea, Kriti, Laos, Libya, Madeira, Massachusetts, Morocco, New Hampshire, New York, New Zealand North, Oregon, Pakistan, Pennsylvania, Peru, Poland, Portugal, South European Russi, Spain, Tibet, Trinidad-Tobago, Tunisia, Vietnam, Washington, West Himalaya
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:30478388-2
1
|
This is the common grape which has a lot of varieties but only a few are grown (commercially). Common Grape Vine (Vitis vinifera) is a species of grapevine native to the Mediterranean region, central Europe, and southwestern Asia. It is a woody perennial vine that grows to a length of 20-30 feet when supported by a trellis or other structure. The leaves are dark green and palmately lobed, with five to nine leaflets. The flowers are small and greenish-white, and are produced in clusters. The fruit is a berry, typically blue or purple in color, and is edible. In terms of growth and cultivation, Common Grape Vine prefers full sun and well-draining soil. It can be grown from cuttings or from grape seeds, and should be trained to a trellis or other support structure. In order to produce fruit, the plant must be cross-pollinated with another grapevine of a different variety. The fruit is typically harvested in the late summer or early fall. The edible fruit of the Common Grape Vine can be eaten fresh or used to make wine, juice, and other products. The fruit can be stored by freezing or canning. The leaves can also be eaten, and are commonly used in dishes such as dolma. In addition to its edible fruit, the Common Grape Vine has several other uses. The leaves can be used as a source of natural dye, and the wood can be used for fuel or to make furniture and other items. The plant also provides habitat and food for a variety of wildlife, including birds and small mammals. Fruits are used to be eaten fresh or used for producing juice, wine or vinegar. Raisins are made out of dried grapes. Leaves and flowers can be eaten too. Seeds are used to produce oil. # Propagation While propagation from seed is possible, propagating from cuttings or grafting is way more common and simple. |
Show
Edit |

|
Tansy |
3-8
Full sun
Dry, Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
1.0
0.5
Perennial
Herbs
Fast
true
Flowers, Leaves
Common tansy, golden buttons, curly leaf tansy
Rainfarn
Asteraceae or compositae
Albania, Altay, Amur, Austria, Baltic States, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Buryatiya, Central European Rus, Chita, Corse, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, East European Russia, Finland, France, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Hungary, Inner Mongolia, Irkutsk, Italy, Japan, Kamchatka, Kazakhstan, Khabarovsk, Kirgizstan, Korea, Krasnoyarsk, Krym, Kuril Is., Magadan, Manchuria, Mongolia, Netherlands, North Caucasus, North European Russi, Northwest European R, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Primorye, Romania, Sakhalin, Sicilia, South European Russi, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Transcaucasus, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Tuva, Ukraine, West Siberia, Xinjiang, Yakutskiya, Yugoslavia
Alaska, Alberta, Arizona, Arkansas, Bolivia, Brazil North, Brazil Northeast, Brazil South, Brazil Southeast, Brazil West-Central, British Columbia, California, Colombia, Colorado, Connecticut, Cook Is., Ecuador, Føroyar, Georgia, Iceland, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Ireland, Kansas, Kentucky, Labrador, Louisiana, Maine, Manitoba, Maryland, Massachusetts, Mauritius, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New South Wales, New York, Newfoundland, North Carolina, North Dakota, Northwest Territorie, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Oklahoma, Ontario, Oregon, Panamá, Paraguay, Pennsylvania, Peru, Prince Edward I., Queensland, Québec, Rhode I., Réunion, Saskatchewan, South Australia, South Dakota, Tasmania, Tennessee, Trinidad-Tobago, Tubuai Is., Uruguay, Utah, Venezuela, Vermont, Victoria, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tansy
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Tanacetum vulgare
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:252568-1
0.2
Weed potential
Condiment, Tea
Compost, Dye, Essential Oil, Pest control, Strewing, Dynamic accumulator, Fragrance
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
Northern Highbush Blueberry |
3-8
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Acidic
Deciduous
2.0
1
Perennial
Shrubs
Medium
Animal feed, Attracts insects, Hedgerow, Wildlife habitat
true
Fruit, Leaves
Blue huckleberry, tall huckleberry, swamp huckleberry, high blueberry, swamp blueberry, american blueberry, blueberry, blue rose tree, bluerose
Heidelbeere
Ericaceae
Alabama, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Oklahoma, Ontario, Pennsylvania, Québec, Rhode I., South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Vermont, Virginia, West Virginia
British Columbia, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Poland, Washington, Wisconsin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vaccinium_corymbosum
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Vaccinium corymbosum
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:261823-2
0.4
Tea
|
Northern Highbush Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) is a type of blueberry plant native to the eastern and central United States and Canada. It is a shrub that typically grows to a height of 5-12 feet, with a spreading, upright habit. The leaves are deciduous, elliptical in shape, and about 2-3 inches long. The flowers are white, bell-shaped, and about ¼ inch long. The fruit is a small, round, blue-black berry that is edible and delicious. Northern Highbush Blueberry is typically grown in well-drained, acidic soil in full sun. It requires regular watering and pruning to maintain its shape and promote fruit production. The plant can be differentiated from similar plants by its white flowers, elliptical leaves, and blue-black berries. The edible fruit of Northern Highbush Blueberry can be stored after harvest by freezing or drying. The plant has a number of uses, including as a source of fresh fruit, in jams and jellies, and in baking. It is also prized for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and has been used in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments. Northern Highbush Blueberry is an important food source for a variety of wildlife, including birds and small mammals. The plant is valued for its ability to attract pollinators, and for its contributions to soil health and ecosystem diversity. |
Show
Edit |

|
Black mulberry |
5-9
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Deciduous
10.0
4.5
Perennial
Trees
Slow
Dye, Fiber, Lumber
true
Fruit, Shoots
Mulberry, Morus species
Schwarze maulbeere
Moraceae
Iran
Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Bermuda, Bulgaria, Canary Is., Cuba, Greece, India, Iraq, Italy, Kazakhstan, Kirgizstan, Kriti, Lebanon-Syria, Leeward Is., Libya, Madeira, Morocco, Puerto Rico, Romania, Spain, Tadzhikistan, Transcaucasus, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, West Himalaya, Windward Is., Xinjiang
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morus_nigra
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Morus nigra
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:854688-1
|
The black mulberry (Morus nigra) is a species of mulberry native to southwestern Asia, including Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. It is a small to medium-sized tree that grows to be about 20-30 feet tall and has a round, dense canopy. The leaves of the black mulberry are dark green and glossy on the top, and paler and slightly hairy on the bottom. The tree produces small, white flowers in the spring, which are followed by black, juicy fruits in the summer. The black mulberry is relatively fast-growing and can reach its full size in about 10-15 years. It prefers well-drained, fertile soil and full sun, but can tolerate partial shade. It is also winter hardy and can withstand temperatures down to about -10°F. The fruits of the black mulberry are edible and can be eaten fresh or used in jams, jellies, and other preserves. They can also be dried and stored for later use. The leaves of the black mulberry can be fed to silkworms, and the wood of the tree is strong and durable, making it suitable for a variety of uses. In addition to its edible fruits, the black mulberry has several other uses. Its leaves can be used as a natural fertilizer, and the tree can provide shade and wind protection in gardens and farms. The black mulberry is also a popular food source for birds and other wildlife. |
Show
Edit |

|
White mulberry |
3-9
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Deciduous
18
13
Perennial
Trees
Medium
Biomass, Dye, Fiber, Animal feed, Wind breaker, Tannin, Lumber
true
Fruit, Inner bark, Leaves, Shoots
Common mulberry
Weiße Maulbeere
Moraceae
Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Central African Repu, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Liberia, Mauritania, Namibia, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, Uganda, Zaïre
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morus_alba
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Morus alba
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:547653-1
Weed potential
Manna, Tea
|
The white mulberry is a deciduous tree native to northern China, Korea, and Japan. It has large, heart-shaped leaves and small, white or pale pink flowers that grow in clusters. The tree can grow to be quite large, up to 50 feet tall, and it is fast-growing. White mulberry trees can be differentiated from other mulberry trees by their white, rather than dark purple, fruit. White mulberry trees prefer well-draining soil and full sun, but can tolerate partial shade. They are drought-tolerant and can thrive in a variety of soil types. In colder climates, they may need to be protected from frost during the winter months. The fruit of the white mulberry tree is edible and is often used to make jams, jellies, and wines. The fruit can be stored by freezing or canning. Young leaves can also be eaten. White mulberry trees are valued for their fast growth and ability to provide shade. They can be used for wind protection and as a ground cover. The leaves of the tree are sometimes used as animal feed. In some cultures, the bark of the white mulberry tree is used medicinally. Leaves are not frost resistant. |
Show
Edit |

|
Red mulberry |
4-9
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
15.0
4.5
Perennial
Trees
true
Fruit, Leaves, Shoots
Common mulberry, white mulberry
Rote maulbeere
Moraceae
Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Ontario, Pennsylvania, Rhode I., South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Vermont, Virginia, West Virginia, Wisconsin
Bermuda, New Mexico, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morus_rubra
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Morus rubra
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:854710-1
1.5
Fiber, Lumber
|
The Red mulberry, Morus rubra, is native to the eastern United States and Canada. It is a deciduous tree that can grow to a height of up to 80 feet. The leaves are dark green and have a rough texture. The tree produces small, greenish-white flowers in the spring, which develop into clusters of red berries in the summer. The Red mulberry is often differentiated from other mulberry species by its smaller leaves and red berries. It prefers well-drained, moist soil and partial to full sun exposure. It is winter hardy and does not require any special care or maintenance. The fruit of the Red mulberry is edible and can be eaten fresh or used in cooking and baking. The berries can be stored in the refrigerator for up to a week. The tree also has a number of medicinal uses, including as a laxative and for treating sore throat and bronchitis. In terms of wildlife, the Red mulberry is a valuable food source for a variety of birds and mammals. Its fruit is a popular food source for birds such as robins, mockingbirds, and blue jays. The tree also provides habitat for birds and small mammals. |
Show
Edit |