Permaculture companion plants for Onion
| Image | Name | Data | Description | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Beet |
4-8
Biennial
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Deciduous
0.9
True
Leaves, Root
Seed - direct sow, Seed - transplant
2 weeks before last frost
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/beta_vulgaris
Chenopodiaceae
Rübe
https://pfaf.org/user/plant.aspx?latinname=beta vulgaris craca
6.0-6.8
10°c (50°f)
5-12 days
1.5 cm
20cm
45-65
Beta vulgaris subsp. vulgaris Conditiva Group, beetroot
6-8 weeks before last frost
2-3 weeks before last frost, 6-8 weeks before the first frost
2-3 years
0.25
|
Beet (Beta vulgaris vulgaris), also known as garden beet, red beet, or table beet, is a plant that is native to the Mediterranean region. It is a biennial plant that typically grows to a height of 0.5-1.5 feet and has dark green leaves that are long and rounded, with a smooth or slightly hairy texture. The stem is usually light green in color, and the plant produces small, white or yellow flowers. Beet plants grow best in well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter, and they prefer full sun to partial shade. To cultivate beets successfully, a grower will need to keep the soil moist and weed-free, and may need to thin the plants to allow for proper growth. Beets are edible, and the most commonly eaten part of the plant is the root, which is typically red or purple in color. The leaves of the plant can also be eaten, and are often used in salads. Beets can be stored after harvest by washing and trimming the roots, and then storing them in a cool, dark place. Beets have a number of uses, both culinary and non-culinary. In the kitchen, beets can be cooked in a variety of ways, including boiling, roasting, and grilling. They can also be used to add color and flavor to salads, soups, and stews. In addition to their culinary uses, beets have a number of medicinal properties and have been used to treat a variety of ailments, including indigestion, constipation, and inflammation. Beets are also valuable for their ability to improve soil fertility, as their leaves and roots contain high levels of nitrogen and other nutrients. They can be used as a natural fertilizer, and can also be used as a mulch or as a ground cover to help control weeds. Beets are not particularly attractive to wildlife, but they can provide food for a variety of animals, including deer, rabbits, and birds. Overall, beets are a versatile and valuable plant that is widely cultivated by gardeners and farmers for their edible roots and leaves, as well as for their potential uses in medicine and agriculture. ### Links [How to Grow Beets @ Harvest to Table](https://harvesttotable.com/how_to_grow_beets/) |
Show
Edit |

|
Carrot |
3-10
Biennial
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
1.2
Leaves, Root
Apiaceae or Umbelliferae
Möhre, Karotte
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Daucus carota sativus
Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Austria, Azores, Baleares, Baltic States, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canary Is., Cape Verde, Central European Rus, China South-Central, China Southeast, Corse, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, East Aegean Is., East European Russia, Eritrea, Ethiopia, France, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Hungary, Iran, Iraq, Ireland, Italy, Kazakhstan, Kirgizstan, Kriti, Krym, Lebanon-Syria, Libya, Madeira, Morocco, Nepal, Netherlands, North Caucasus, Northwest European R, Norway, Pakistan, Palestine, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Sardegna, Sicilia, South European Russi, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Transcaucasus, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, West Himalaya, Yugoslavia
Alabama, Amsterdam-St.Paul Is, Andaman Is., Angola, Argentina Northeast, Argentina Northwest, Argentina South, Arizona, Arkansas, Bangladesh, Brazil South, British Columbia, California, Cape Provinces, Chile Central, Chile South, China North-Central, Colorado, Connecticut, Costa Rica, Cuba, Delaware, Desventurados Is., District of Columbia, Dominican Republic, Easter Is., Ecuador, El Salvador, Finland, Florida, Georgia, Guatemala, Hainan, Haiti, Iceland, Idaho, Illinois, India, Indiana, Inner Mongolia, Iowa, Jamaica, Japan, Jawa, Kansas, Kentucky, Kermadec Is., Korea, Labrador, Leeward Is., Louisiana, Maine, Manchuria, Manitoba, Marianas, Marshall Is., Maryland, Massachusetts, Mauritius, Mexico Central, Mexico Northeast, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Mongolia, Montana, Myanmar, Nebraska, Nevada, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, New Zealand North, New Zealand South, Newfoundland, Nicobar Is., North Carolina, North Dakota, North European Russi, Northern Provinces, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Oklahoma, Ontario, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Peru, Primorye, Prince Edward I., Puerto Rico, Qinghai, Québec, Rhode I., Rodrigues, Réunion, Saskatchewan, South Carolina, South Dakota, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Tasmania, Tennessee, Texas, Tibet, Trinidad-Tobago, Uruguay, Utah, Vermont, Vietnam, Virginia, Washington, West Siberia, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming, Xinjiang
0.20
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:841063-1
|
Carrot (Daucus carota sativus) is a type of root vegetable that is native to Europe and Asia. It belongs to the family Apiaceae, which includes around 300 species of plants. Carrots are a popular crop, known for their sweet, crunchy roots and vibrant orange color. The plant has a tall, slender growth habit and can reach a height of up to 2-3 feet. The leaves are green and feathery, and the flowers are small and white or purple in color. To grow carrots successfully, it is important to choose a location with well-drained, sandy soil and full sun. The plant prefers cool temperatures and should be protected from frost. Carrots can also be grown in containers, and will benefit from regular watering and fertilization. The plant is relatively easy to grow and requires little maintenance, but can be susceptible to pests and diseases, such as carrot fly and root rot. Carrots are a valuable source of vitamins and minerals, and are used in a variety of dishes, including soups, stews, and salads. The roots can be eaten fresh or cooked, and can be stored in the refrigerator for several weeks. In addition to their culinary uses, carrots have a number of medicinal properties, and have been used to treat a variety of ailments, including indigestion, constipation, and respiratory disorders. Carrots are also a valuable food source for many types of wildlife, including birds, insects, and small mammals. The flowers attract bees and other pollinators, and the roots are eaten by animals such as rabbits and deer. |
Show
Edit |

|
Chard |
4-8
Biennial
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
0.9
true
Leaves, Stem
Chenopodiaceae
Swiss chard, silver beet, perpetual spinach, beet spinach, seakale beet, leaf beet
Mangold, krautstiel
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Beta vulgaris cicla
2-3 years
|
Leaf vegetable. Leaves and stalks are edible. Closely related to the beet. |
Show
Edit |

|
Tomato |
10-12
Annual, Perennial
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
2.0
True
Fruit, Seed
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tomato
Fast
Garden tomato, Dumádu, Garden tomato, Love apple, Lycopersicum esculentum, Tomate, Tomato, Tomato extract containing lycopene, Tomato|thakkali, Tumatis, Lycopersicon esculentum
Solanaceae
Tomate
Oil
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Solanum lycopersicum, https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Lycopersicon esculentum
Start seeds indoors 5-6 weeks before last frost
In containers or in rows in beds around last frost date
6.2-6.8
70-80°f
Peru
Alabama, Alaska, Andaman Is., Angola, Arizona, Arkansas, Assam, Austria, Azores, Bahamas, Bangladesh, Belarus, Benin, Bolivia, British Columbia, Bulgaria, Burkina, California, Cambodia, Cameroon, Canary Is., Cape Verde, Caroline Is., Central African Repu, Chagos Archipelago, Chatham Is., Christmas I., Colombia, Comoros, Connecticut, Cook Is., Costa Rica, Cuba, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, Delaware, Dominican Republic, East Aegean Is., East European Russia, East Himalaya, Ecuador, Fiji, Florida, Galápagos, Georgia, Gilbert Is., Gulf of Guinea Is., Haiti, Hawaii, Illinois, India, Indiana, Iowa, Ivory Coast, Jawa, Kansas, Kazakhstan, Kentucky, Korea, Laccadive Is., Laos, Leeward Is., Line Is., Louisiana, Madagascar, Madeira, Maine, Malawi, Mali, Marianas, Marquesas, Marshall Is., Maryland, Massachusetts, Mauritania, Mauritius, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Mozambique, Myanmar, Namibia, Nansei-shoto, Nauru, Nebraska, Nepal, Nevada, New Brunswick, New Caledonia, New Hampshire, New York, New Zealand North, Nicaragua, Nicobar Is., Niue, North Carolina, North Dakota, Nova Scotia, Ogasawara-shoto, Ohio, Ontario, Oregon, Pakistan, Panamá, Pennsylvania, Philippines, Pitcairn Is., Puerto Rico, Québec, Rhode I., Réunion, Saskatchewan, Selvagens, Society Is., South Carolina, South European Russi, Tadzhikistan, Taiwan, Tennessee, Texas, Trinidad-Tobago, Tuamotu, Tubuai Is., Turkey, Turkmenistan, Tuvalu, Utah, Uzbekistan, Venezuela, Vermont, Vietnam, Virginia, Wake I., Wisconsin, Zambia, Zaïre, Zimbabwe
1.00
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:316947-2
|
The tomato is a flowering plant native to South America. It is a member of the nightshade family and closely related to the potato. The tomato plant typically grows to a height of 1-3 meters and has a weak, hairy stem. The leaves are arranged alternately on the stem and are typically dark green in color. The plant produces small yellow or white flowers, which develop into the fruit we know as tomatoes. The fruit itself is typically red, but can also be yellow, orange, green, or purple. Indeterminate tomato plants are perennials in their native habitat, but are cultivated as annuals. Determinate, or bush, plants are annuals that stop growing at a certain height and produce a crop all at once. Tomatoes prefer warm, sunny growing conditions and well-drained, humus-rich soil. They can be grown in a variety of soil types, but perform best in soil with a pH between 6 and 6.8. In order to cultivate tomatoes successfully, growers may need to provide support for the plant (such as a stake or cage) to prevent the fruit from weighing down the stem, and may also need to water and fertilize the plant regularly. Tomatoes are generally considered to be frost-sensitive, so in areas with cold winters they may need to be grown in a greenhouse or indoors. There are a great number of cultivars. The edible parts of the tomato plant are the fruit and the leaves. The fruit can be eaten raw or cooked, and is commonly used in a variety of dishes, such as salads, sandwiches, and pasta. The leaves, although not commonly eaten, are also edible and have a slightly bitter taste. After harvest, tomatoes can be stored at room temperature, in a cool place, or in the refrigerator. |
Show
Edit |
|
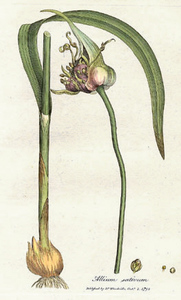
Garlic |
3-10
Perennial
Full sun
Dry, Moist
Light (sandy), Medium
0.6
Herbs
Bulb, Flowers, Leaves, Root, Seed
Seed - direct sow
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Garlic
Cultivated garlic
Alliaceae
Knoblauch
20cm
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Allium sativum
6.5-7.0
Sting and itch relief from insect bites
Fibrous
Shallow
100-150
Allium
Iran, Kazakhstan, Kirgizstan, Tadzhikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan
Albania, Algeria, Amur, Austria, Baleares, Baltic States, Bangladesh, Belarus, Bulgaria, Cambodia, Canary Is., Central European Rus, China North-Central, China South-Central, China Southeast, Corse, Cuba, Czechoslovakia, Dominican Republic, East European Russia, Egypt, Ethiopia, France, Galápagos, Germany, Greece, Haiti, Hungary, Illinois, India, Iraq, Italy, Jamaica, Kentucky, Korea, Leeward Is., Libya, Mexico Central, Mexico Northwest, Mexico Southeast, Mexico Southwest, Morocco, New York, North European Russi, Northwest European R, Pakistan, Poland, Primorye, Puerto Rico, Romania, Sardegna, Seychelles, Sicilia, South European Russi, Spain, Switzerland, Tennessee, Thailand, Trinidad-Tobago, Tunisia, Turkey, Ukraine, Vermont, Wisconsin, Yugoslavia
Late autumn, Early spring
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:528796-1
|
Garlic (Allium sativum) is a bulbous perennial plant in the family Amaryllidaceae. It is native to central Asia and northeastern Iran, and has long been a staple in cuisines around the world. The plant has a distinctive appearance, with narrow, long leaves and a tall, hollow stem. The leaves are a pale green color and are attached to the stem in a spiral arrangement. The flowers are small and white, and are clustered in a spherical head at the top of the stem. Garlic plants can grow to a height of 30-150 cm (12-59 in), depending on the variety. They are relatively fast-growing plants, with the bulbs maturing in about seven months. Mulch for proper overwintering when planted in autumn. Garlic can be differentiated from other plants in the Allium genus by its distinctive flavor and aroma. It is also often distinguished by its long, narrow leaves and tall, hollow stem. Garlic prefers well-drained soil and full sun, and is typically grown from bulbs. To cultivate garlic successfully, growers should plant the bulbs in the fall, about 6-8 weeks before the first frost. The bulbs should be spaced about 10-15 cm (4-6 in) apart, with the pointed end facing up. After planting, the bulbs should be watered regularly and mulched to protect them from cold temperatures. Garlic is edible, with the bulbs and leaves being the most commonly eaten parts of the plant. The bulbs can be used fresh or cooked, and are often used as a seasoning in a wide variety of dishes. The leaves can be used fresh or cooked, and have a milder flavor than the bulbs. To harvest dig and do not pull out the bulbs. Let them dry in an airy, shady and dry spot e.g. by hanging them up. Once wrappers are dry, it can be stored at a dry place for several months. In addition to its culinary uses, garlic has a number of other uses. It is commonly used medicinally, as it has been shown to have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. It is also sometimes used as a natural insect repellent. In the garden, it can be used as a natural fertilizer, as it is believed to improve the soil and help deter pests. Garlic has value for wildlife, as it is attractive to a wide variety of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. It is also a food source for animals such as rabbits and deer. |
Show
Edit |

|
Broccoli |
2-11
Annual, Biennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
0.9
Flowers, Leaves
Brassicaceae or Cruciferae
Brokkoli
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Brassica oleracea italica
50-100
45cm
6.0-7.0
7-10 days
4°C (40°F)
6-8 weeks before last frost
3 to 7 years
|
Broccoli is a plant that is native to the Mediterranean region. It is part of the Brassica oleracea family, which also includes other vegetables such as cauliflower and cabbage. Broccoli plants have green, flowering heads that are similar in appearance to cauliflower. The stems are typically thick and can grow to be quite large, depending on the variety of broccoli. The leaves of the plant are typically dark green and are arranged in a spiral pattern along the stem. When it comes to growing conditions, broccoli prefers cool weather and well-draining soil. It is a relatively fast-growing plant, with the flowering heads typically forming in the first year. To cultivate broccoli successfully, a grower will need to make sure the plant gets enough water and sunlight, and provide it with the necessary nutrients through fertilization. In terms of winter hardiness, broccoli is not very frost-tolerant, so it is typically grown as a cool-season crop in areas with mild winters. In terms of edibility, broccoli is a very nutritious vegetable that is packed with vitamins and minerals. The flowering heads and the stems are both edible, and can be cooked in a variety of ways. After harvest, broccoli can be stored in the refrigerator for several days, or frozen for longer-term storage. ### Propagation - Direct sow Sow seeds 7cm apart, thin when seedlings reach 5-7cm in height. ### Propagation - Transplant Start seeds 6-8 weeks before your last frost date, or 2-3 weeks before last frost date. Plant outside when seedlings are 4-6 weeks old, or have 4-5 leaves. #### Links [Broccoli @ Almanac](https://www.almanac.com/plant/broccoli) |
Show
Edit |

|
Cucumber |
9-11
Annual
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
2
Vines
Fruit, Leaves
Seed - direct sow, Seed - transplant
1 week after last frost
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cucumber
Cucurbitaceae
Gurke
50-65
23cm
6.0-6.8
15-30°C (60-85°F)
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Cucumis sativus
True
Fruit
Assam, Bangladesh, China South-Central, China Southeast, East Himalaya, Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand, West Himalaya
Alabama, Albania, Andaman Is., Arizona, Arkansas, Austria, Bahamas, Bolivia, Caroline Is., Cayman Is., Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Florida, Georgia, Gulf of Guinea Is., Haiti, Illinois, India, Jamaica, Kansas, Kazakhstan, Kentucky, Korea, Laos, Leeward Is., Louisiana, Marianas, Marshall Is., Massachusetts, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, New Caledonia, New York, Nicaragua, Nicobar Is., North Carolina, North Caucasus, Ohio, Oman, Ontario, Pakistan, Pennsylvania, Pitcairn Is., Puerto Rico, South Carolina, Sri Lanka, Sweden, Tadzhikistan, Trinidad-Tobago, Turkmenistan, Utah, Uzbekistan, Venezuela, Vietnam, Virginia, Windward Is., Zaïre
2-3 weeks before last frost
1 week after last frost
0.9
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:292296-1
|
Cucumber, scientific name Cucumis sativus, is a member of the gourd family. It is native to India and other parts of Asia. Cucumber is a trailing or climbing plant that grows to a height of 5-10 feet. The leaves are dark green and glossy, and the plant produces yellow flowers. The fruit of the cucumber plant is a long, green, edible vegetable with a thin skin. Cucumbers are typically about 6-9 inches long and 2-3 inches in diameter. In terms of growth and cultivation, cucumber plants prefer warm, sunny conditions and well-draining soil. They should be watered regularly, especially during dry periods. Cucumber plants are not winter hardy and should be grown in the summer months in most climates. To cultivate cucumbers successfully, it is important to provide them with adequate space to grow and to support the plants with trellises or other means to keep the fruits off the ground. The plant will develop male and female flowers. You can recognize the female by having a tiny cucumber underneath. Sometimes the plant develops a lot of male flowers first, so be patient. If you don’t see any bees pollinating. Take a male and put it on all the female flowers. Cucumber fruits are edible and can be eaten raw, pickled, or cooked. The skin and seeds of the cucumber are edible, but some people choose to remove the seeds before eating the fruit. Cucumber fruits can be stored in the refrigerator for a few days after harvest. Cucumbers have several uses. In addition to being eaten as a vegetable, they can also be used in a variety of dishes and salads. Cucumber slices are often used as a garnish or as a refreshing addition to beverages. Cucumbers are also commonly used in natural skin care products and are believed to have anti-inflammatory and soothing properties. #### Propagation Direct sow when soil is warm enough in early summer. Sow seeds individually indoors 3-4 weeks before planting outside into warm soil. Use bottom heat if possible. Transplant when plants develop third leaf. #### Medicinal Fruit is depurative, diuretic, emollient, purgative and resolvent #### Links [Cucumber @ West Coast Seeds](https://www.westcoastseeds.com/products/patio-snacker) |
Show
Edit |

|
Bell pepper |
true
Medium
Moist
Full sun
10-11
Cayenne pepper, chili pepper, christmas pepper, red pepper, ornamental chili pepper
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Solanaceae
1.0
Paprika, gemüsepaprika
Flowers, Fruit, Leaves
Perennial
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Capsicum annuum
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
Jalapeño Chili |
0.6
Annual
Jalapeño
Solanaceae
|
Can be eaten green. |
Show
Edit |

|
Habanero |
Solanaceae
|
The habanero is a hot variety of chili pepper. Unripe habaneros are green, and they color as they mature. The most common color variants are orange and red, but the fruit may also be white, brown, yellow, green, or purple. Typically, a ripe habanero is 2–6 cm (0.8–2.4 in) long. Habanero chilis are very hot, rated 100,000–350,000 on the Scoville scale. The habanero's heat, flavor and floral aroma make it a popular ingredient in hot sauces and other spicy foods. |
Show
Edit |

|
Rose |
2
Perennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Deciduous
Shrubs
Animal feed, Attracts insects, Hedgerow, Wind breaker, Wildlife habitat
True
Fruit
Rosaceae
Zambia
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:77120313-1
1
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
Lettuce |
5-9
Annual, Biennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium
0.9
Herbs
true
Leaves, Seed
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lettuce
Garden lettuce
Asteraceae or compositae
Blattsalat
Oil
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Lactuca sativa
Iraq
Alabama, Antipodean Is., Argentina Northeast, Assam, Austria, Baleares, Baltic States, Bangladesh, Belize, Bolivia, Bulgaria, Burkina, California, Cameroon, Canary Is., Cape Provinces, Cape Verde, Caroline Is., Central European Rus, Chad, China North-Central, Colombia, Connecticut, Corse, Costa Rica, Cuba, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, Delaware, District of Columbia, Dominican Republic, East European Russia, East Himalaya, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Fiji, Finland, France, Free State, Germany, Great Britain, Guatemala, Haiti, Hawaii, Honduras, Hungary, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Inner Mongolia, Ireland, Italy, Jamaica, Jawa, Kazakhstan, Khabarovsk, Korea, Krym, Lebanon-Syria, Madeira, Maine, Marianas, Marshall Is., Massachusetts, Mauritania, Mauritius, Mexico Southeast, Michigan, Missouri, Myanmar, Nepal, Netherlands, New Guinea, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Nicaragua, Niue, North Carolina, North Caucasus, North Dakota, North European Russi, Northwest European R, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oman, Ontario, Oregon, Pakistan, Panamá, Paraguay, Pennsylvania, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Primorye, Puerto Rico, Rhode I., Romania, Réunion, Sardegna, Sicilia, South European Russi, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Transcaucasus, Trinidad-Tobago, Tubuai Is., Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Venezuela, Vermont, Vietnam, Wake I., Washington, West Virginia, Yugoslavia
30cm
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:228239-1
|
Lettuce, Lactuca sativa, is a plant native to the Mediterranean region. It has green, elongated leaves that form a loose head. The stem is relatively short and the plant grows to a height of about 8-12 inches. Lettuce is a fast-growing plant, with some varieties able to be harvested in as little as 45 days. Lettuce can be differentiated from similar plants by its elongated leaves and loose head formation. It is also relatively short compared to other leafy green plants like kale and spinach. Lettuce prefers cool temperatures and grows best in full sun or partial shade. It is a hardy plant and can tolerate light frost, but will not survive extreme cold. To cultivate lettuce successfully, growers should ensure that the soil is well-drained and moist, and that the plants are spaced appropriately. Lettuce is edible and the leaves can be eaten raw in salads or cooked. The leaves can also be stored by washing and drying them, and then wrapping them in a damp paper towel before placing them in the refrigerator. Lettuce has a number of uses. It is a popular ingredient in salads and other dishes, and has been used medicinally to treat a variety of ailments, including insomnia and digestive issues. |
Show
Edit |

|
Marjoram |
6-9
Perennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Dry, Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
0.6
Herbs
true
Leaves
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marjoram
Lamiaceae or labiatae
Majoran
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Origanum majorana
Cyprus, Turkey
Algeria, Azores, Baleares, Baltic States, Corse, Czechoslovakia, Great Britain, Greece, India, Italy, Juan Fernández Is., Krym, Libya, Madeira, Morocco, Spain, Switzerland, Tunisia, Ukraine, Venezuela, Yugoslavia
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:453303-1
|
Marjoram (Origanum majorana) is a herbaceous plant that is native to the Mediterranean region. It has delicate, oval-shaped leaves that are pale green in color, and small white or pink flowers that grow in clusters. The plant grows to a height of about 30 cm and has a woody stem. In terms of growing conditions, marjoram prefers well-drained, light soil and full sun to partial shade. It can be grown from seeds or cuttings, and should be spaced about 30 cm apart. Marjoram is winter hardy in mild climates, but may need to be protected or brought indoors in colder regions. Marjoram has a number of culinary uses. It is often used as a flavoring in soups, stews, and sauces, and can be added to salads and other dishes as a garnish. The leaves and flowers of the plant are edible and can be used fresh or dried. When harvesting marjoram, it is best to pick the leaves early in the morning when they are at their most flavorful. The leaves can be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dark place for up to six months. In addition to its culinary uses, marjoram has also been used medicinally as an antiseptic and as a remedy for digestive problems. It is also sometimes used in perfumes and soaps. Marjoram is not particularly attractive to wildlife, but it can provide habitat for some beneficial insects such as bees and butterflies. |
Show
Edit |

|
Parsley |
5-8
Biennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
0.6
Herbs
true
Leaves
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parsley
Medium
Apiaceae or umbelliferae
Petersilie
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Petroselinum crispum
Algeria
Greece, Morocco, Yugoslavia
15cm
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:60442790-2
|
Parsley is a herb native to the central and eastern Mediterranean region. It has bi-pinnate leaves and small, white or green flowers. The plant grows to a height of about 30 cm and has a fast growth rate. It can be differentiated from similar plants by its bi-pinnate leaves and small, white or green flowers. Parsley prefers well-drained soil and full sun to partial shade. To cultivate it successfully, a grower may need to water it regularly and protect it from frost. The plant is winter hardy and can withstand cold temperatures. Parsley is edible and its leaves and stems can be used in cooking. The edible parts can be stored after harvest by drying or freezing. Parsley has many uses, including medicinal and culinary. It has been used to treat a variety of ailments, such as indigestion and inflammation. In the kitchen, it can be used as a garnish or added to dishes for flavor. Parsley is also a good source of vitamins and minerals, such as vitamins A and C and iron. Parsley is valuable for wildlife as it provides nectar for pollinators. It is also a good source of food for some animals, such as rabbits and deer. #### Links [Parsley @ Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parsley) |
Show
Edit |

|
Parsnip |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parsnip
true
Moist
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
4-8
Wild parsnip
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Apiaceae or umbelliferae
1.0
Pastinake
Roots
Leaves, Root, Seed
Weed potential
Biennial
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Pastinaca sativa
Sicilia
Albania, Altay, Austria, Baltic States, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Central European Rus, Corse, Czechoslovakia, East European Russia, France, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Krasnoyarsk, Krym, Lebanon-Syria, Mongolia, Netherlands, North Caucasus, Poland, Romania, Sardegna, South European Russi, Spain, Switzerland, Transcaucasus, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Ukraine, West Siberia, Yugoslavia
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:845768-1
0.4
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
Passion fruit |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Passiflora_edulis
true
Fast
Moist
Full sun
9-12
Vines
Purple granadilla, passion fruit, granadilla, aul aanp, bai xiang guo, buah negeri, buah susu, garendal, granadiglia, granadilho, grenadille, ji dan guo, kudamonotokeiso, liliko'i, linmangkon, louki, magalendendele, maracuja-roxo, maracuya, markisa, maseche, matunda, munchi, obutunda, pasionaria, purpurgrenadille, qaranidila, sawarot, soh-brap, tikeiso, common passionfruit, fleur de la passion, flor de la pasión, granadiglia incarnata, granadilla, grenadella, kalala, maracayú, maracujá, maracujá azedo, maracujá-comum, maracujá-de-comer, maracujá-de-ponche, maracujá-do-mato, maracujá-doce, maracujá-mirim, maracujá-peroba, maracujá-preto, maracujá-redondo, maracuya, pasiflora, passiflora, passiflorae acetum folium, passiflore, passion flower, passion fruit, passion fruit|wel dodam, passionsblume, passionsfrukt, purple granadilla, purple passionflower
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Passifloraceae
9.0
Oil
Weed potential
Fruit
Perennial
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Passiflora edulis
Argentina Northeast, Brazil Northeast, Brazil South, Brazil Southeast, Brazil West-Central, Paraguay
Angola, Argentina Northwest, Assam, Azores, Bangladesh, Benin, Bolivia, Borneo, Brazil North, Burundi, Cambodia, Cameroon, Canary Is., Caroline Is., Central African Repu, China South-Central, China Southeast, Colombia, Comoros, Cook Is., Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominican Republic, East Himalaya, El Salvador, Ethiopia, Fiji, Florida, Gabon, Galápagos, Gambia, Gilbert Is., Guatemala, Gulf of Guinea Is., Hawaii, Honduras, India, Jamaica, Jawa, Kenya, KwaZulu-Natal, Laos, Leeward Is., Lesser Sunda Is., Malawi, Malaya, Marianas, Marshall Is., Mauritius, Mexico Central, Mexico Northeast, Mexico Southeast, Mexico Southwest, Morocco, Mozambique, New Caledonia, New South Wales, New Zealand North, Norfolk Is., Northern Provinces, Panamá, Peru, Puerto Rico, Queensland, Rodrigues, Réunion, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Swaziland, Taiwan, Tanzania, Thailand, Tonga, Trinidad-Tobago, Uganda, Venezuela, Victoria, Vietnam, West Himalaya, Windward Is., Zambia, Zaïre, Zimbabwe
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:321964-2
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
Potato |
3-10
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
1.0
0.5
Perennial
12 inches
Seed - direct sow
April
Root
Irish potato, Andigena
Kartoffel
Solanaceae
Argentina Northwest, Argentina South, Bolivia, Chile Central, Chile North, Chile South, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Venezuela
Assam, Bangladesh, Belgium, Dominican Republic, East European Russia, East Himalaya, France, Great Britain, Haiti, Hawaii, Illinois, India, Ireland, Laos, Maryland, Minnesota, New York, South European Russi, Tadzhikistan, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, Zaïre
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potato
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Solanum tuberosum
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:821337-1
|
Potato (Solanum tuberosum) is a herbaceous perennial plant that is native to the Andean region of South America. It is a member of the nightshade family (Solanaceae) and is closely related to other nightshades such as tomatoes, eggplants, and bell peppers. The potato plant has a bushy growth habit and can grow to heights of 30-150 cm depending on the variety. The leaves are large, heart-shaped, and alternate along the stem. The flowers are white or purple and have five petals. The plant produces small green berries that contain numerous seeds, but most varieties of potatoes are propagated vegetatively from tubers rather than from seeds. The edible part of the potato plant is the tuber, which is an underground stem that is modified for food storage. Potatoes come in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors including white, yellow, red, and purple. The size and shape of the tuber depends on the variety, with some varieties producing small, round tubers and others producing large, elongated tubers. Potatoes grow best in well-draining, fertile soils in a sunny location with a pH of 4.5-6.0. They require regular watering and should be planted in a location with good air circulation to prevent fungal diseases. Potatoes are typically planted from tubers that have been treated with a fungicide to prevent disease and are spaced 25-30 cm apart in rows that are 75-90 cm apart. The tubers will begin to form in the soil around 6-8 weeks after planting and can be harvested when they reach the desired size. Potatoes are a versatile and nutritious food source that is rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. The tubers are eaten cooked, baked, fried, or mashed, and the leaves and flowers of the plant can also be eaten. Potatoes can be stored in a cool, dry, and dark place for several months. Potatoes have a number of uses beyond their value as a food source. The tubers can be used as seed potatoes for planting, and the leaves and stems can be used as a natural insecticide or as mulch in the garden. In some parts of the world, potatoes are also used for their medicinal properties. Potatoes are a valuable food source for a variety of wildlife, including deer, rabbits, and squirrels. The flowers of the potato plant are also a source of nectar for bees and other pollinators. |
Show
Edit |

|
Strawberry |
4-8
Perennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
0.3
Herbs
Ground cover
True
Fruit, Leaves
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strawberry
Rosaceae
Erdbeere
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Fragaria x ananassa
Aardbei
Jordbær
British Columbia, California, Oregon, Washington
Albania, Baltic States, Belarus, Central European Rus, Denmark, East European Russia, El Salvador, Finland, France, Germany, Great Britain, Guatemala, Honduras, Illinois, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Korea, Netherlands, New York, North European Russi, Northwest European R, Norway, Pitcairn Is., South European Russi, Sweden, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Vermont
0.3
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:30117681-2
|
Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) is a popular fruit-bearing plant that is native to parts of the Americas, Europe, and Asia. It is a member of the Rosaceae family and is closely related to other fruit-bearing plants such as raspberries and blackberries. The plant has a low-growing, spreading habit, with leaves that are typically green and glossy, and white flowers that give way to red, juicy berries. The fruits are edible and are often eaten fresh, used in jams and jellies, or baked in desserts. Strawberry plants prefer well-draining, moist soil and plenty of sunlight. They can be grown in a variety of climates, but they tend to thrive in temperate regions with cool summers and mild winters. To cultivate the plants successfully, a grower may need to provide adequate irrigation, fertilizer, and pest control. One of the distinctive features of strawberry plants is their runners, which are long, slender stems that grow horizontally along the ground. These runners can be used to propagate new plants, which can be grown in rows or beds to form a dense, ground-covering mat. In addition to their value as a food source, strawberry plants are also prized for their attractiveness to pollinators and other beneficial insects. They are often used in home gardens and on small farms as a way to attract bees, butterflies, and other insects that help to pollinate other plants. Overall, strawberries are a versatile and valuable plant that is prized by gardeners and farmers alike for their delicious fruit and their ability to attract wildlife. |
Show
Edit |

|
Winter Savory |
6-11
Full sun
Dry, Moist
Light (sandy), Medium
0.4
0.5
Shrubs
Medium
true
Leaves
Bohnenkraut, winterbohnenkraut, bergbohnenkraut
Lamiaceae or labiatae
Albania, Austria, France, Greece, Italy, Lebanon-Syria, Spain, Turkey, Yugoslavia
Azores, Portugal, Texas
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Winter_savory
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Satureja montana
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:457736-1
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
Summer savory |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Summer_savory
true
Dry, Moist
Full sun
5-9
Light (sandy), Medium
Lamiaceae
0.3
Bohnenkraut, gartenbohnenkraut
Leaves
Annual
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Satureja hortensis
Transcaucasus, Turkey
Albania, Altay, Italy, Kazakhstan, Krym, West Himalaya, Xinjiang, Yugoslavia
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:457680-1
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
Kale |
5-10
Biennial, Perennial
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
Deciduous
0.9
Herbs
True
Leaves
Seed - direct sow, Seed - transplant
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kale
Brassicaceae, Cruciferae
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Brassica oleracea acephala
6.0-6.8
Shallow
45cm
7-10 days
0.5 cm
True
Fast
60
4-6 weeks before last frost
At last frost date
3 to 7 years
|
Kale (/keɪl/) is a hardy, leafy green vegetable that is a member of the Brassica oleracea species. It is native to the eastern Mediterranean and Asia Minor, and has been cultivated for food for over 2000 years. Kale plants typically have green or purple leaves that are deeply lobed and can grow up to 2 feet in length. The leaves are attached to a central stem and don't make a head, and the plant produces small, yellow flowers. Kales are considered to be closer to wild cabbage than most of the many domesticated forms of Brassica oleracea. In terms of growing conditions, kale prefers cool weather and does well in full sun to partial shade. It can be grown year-round in mild climates, but in colder climates it is best grown in the fall and early spring. To cultivate kale successfully, it is important to provide the plants with plenty of moisture and to regularly fertilize them. Kale is also a good companion plant for other vegetables, as it can help to deter pests and improve the health of the soil. In terms of edibility, kale is highly nutritious and can be eaten raw or cooked. The leaves and stems are both edible, and the plant can be stored in the refrigerator for several days after harvest. Kale can be used in a variety of dishes, including soups, salads, and smoothies. It can also be cooked and served as a side dish, or used as a garnish. In addition to its culinary uses, kale has a number of other uses. It is often used as a cover crop, as it can help to improve the fertility of the soil. Kale leaves can also be used as a mulch, as they break down readily and release nutrients into the soil. Additionally, kale plants can be used for wind protection, as their large leaves and sturdy stems can provide a barrier to wind. ### Links [Kale @ West Coast Seeds](https://www.westcoastseeds.com/blogs/how-to-grow/grow-kale-collards) |
Show
Edit |

|
Dill |
2-11
Annual
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium
0.8
Herbs
true
Leaves, Seed
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dill
Medium
Apiaceae or umbelliferae
Dill
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Anethum graveolens
Algeria, Chad, Cyprus, Gulf States, Iran, Lebanon-Syria, Libya, Morocco, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia
Afghanistan, Alabama, Albania, Alberta, Altay, Andaman Is., Angola, Argentina Northeast, Arizona, Arkansas, Assam, Austria, Azores, Bahamas, Baleares, Baltic States, Bangladesh, Belarus, Belgium, Brazil South, Brazil Southeast, British Columbia, Bulgaria, California, Cameroon, Canary Is., Cape Verde, Cayman Is., Central European Rus, China North-Central, China South-Central, China Southeast, Connecticut, Costa Rica, Cuba, Czechoslovakia, Delaware, Denmark, Dominican Republic, East Aegean Is., East European Russia, East Himalaya, Ecuador, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Finland, France, Ghana, Great Britain, Greece, Guatemala, Haiti, Hawaii, Hungary, Illinois, India, Indiana, Iowa, Iraq, Italy, Jamaica, Kansas, Kazakhstan, Kentucky, Kenya, Kriti, Krym, Laos, Leeward Is., Louisiana, Madeira, Maine, Manitoba, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Mongolia, Montana, Mozambique, Nebraska, Nepal, Netherlands, New Jersey, New York, Nicobar Is., Niger, Nigeria, North Carolina, North Dakota, Northwest European R, Norway, Ohio, Oklahoma, Ontario, Oregon, Pakistan, Palestine, Pennsylvania, Peru, Portugal, Primorye, Puerto Rico, Québec, Rhode I., Romania, Saskatchewan, Sicilia, Somalia, South Dakota, South European Russi, Spain, Sudan, Sweden, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Tanzania, Texas, Thailand, Transcaucasus, Trinidad-Tobago, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, Virginia, Wake I., Washington, West Virginia, Windward Is., Wisconsin, Yugoslavia
15cm x 30cm
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:837530-1
|
Dill (Anethum graveolens) is a plant native to the eastern Mediterranean region and West Asia. It is an annual herb that grows to a height of about 1-2 feet and has delicate, feathery leaves. The plant has small yellow flowers that bloom in the summer. Dill is a popular herb in many cuisines, especially in European and Middle Eastern dishes. It is used to flavor soups, stews, fish, and pickles. The leaves and seeds of dill are both edible and can be used fresh or dried. The seeds have a more pungent flavor than the leaves and are often used in pickling. Dill can be stored by drying or freezing the leaves and seeds. Dill prefers full sun and well-drained soil. It is easy to grow and can be started from seed or from transplants. Dill is not winter hardy and will die off in the winter. In addition to its culinary uses, dill has been used medicinally to aid in digestion and to reduce inflammation. It has also been used as a natural insect repellent. The plant is attractive to many types of beneficial insects, making it a valuable addition to any garden. |
Show
Edit |

|
Pot marigold |
2-11
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
5.5-7.0
0.6
0.3
Annual
Medium
15cm
6-14 days
21°c (70°f)
60
Repels nematodes
Flowers, Leaves, Seed
Calendula, Common marigold, Scotch marigold, Ruddles
Ringelblume
Asteraceae or compositae
Spain
Afghanistan, Albania, Argentina Northeast, Argentina Northwest, Argentina South, Assam, Austria, Azores, Baleares, Baltic States, Belarus, Belgium, Bolivia, Borneo, British Columbia, Bulgaria, California, Canary Is., Central European Rus, Chatham Is., Chile Central, Chile North, Chile South, China North-Central, China South-Central, China Southeast, Colombia, Connecticut, Cook Is., Corse, Costa Rica, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, East Aegean Is., East European Russia, East Himalaya, Ecuador, Ethiopia, France, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Guatemala, Hainan, Honduras, Hungary, India, Iraq, Ireland, Italy, Jawa, Juan Fernández Is., Kazakhstan, Kriti, Krym, Lebanon-Syria, Lesser Sunda Is., Libya, Madeira, Maine, Malaya, Manchuria, Massachusetts, Mauritius, Mexico Southeast, Michigan, Morocco, Myanmar, Nepal, Netherlands, New Hampshire, New South Wales, New York, New Zealand North, New Zealand South, Newfoundland, North Caucasus, North European Russi, Northern Territory, Northwest European R, Norway, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Ontario, Pakistan, Paraguay, Pennsylvania, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Primorye, Qinghai, Queensland, Québec, Romania, Sardegna, Sicilia, South Australia, South European Russi, Sulawesi, Sumatera, Sweden, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Taiwan, Tasmania, Tibet, Transcaucasus, Trinidad-Tobago, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uruguay, Uzbekistan, Victoria, Vietnam, Washington, Western Australia, Wisconsin, Xinjiang, Yugoslavia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calendula_officinalis
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Calendula officinalis
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:187894-1
4.6
|
The pot marigold, also known as Calendula officinalis, is a flowering plant probably native to southwestern Asia, western Europe, and the Mediterranean region, however, its long cultivation history makes its precise origin unknown. It is a herbaceous annual plant that typically grows to be about 12-18 inches tall, with hairy stems and leaves. The leaves are lance-shaped, with a hairy surface, and the flowers can range in colour from white through yellow and orange to red and even pink. In terms of growing conditions, the pot marigold prefers well-drained soil and full sun, although it can tolerate partial shade. It is winter hardy, but may not flower as profusely in colder climates. To cultivate it successfully, a grower should plant pot marigold seeds directly in the ground after the last frost of the season. The pot marigold has a number of uses, both culinary and medicinal. The flowers are edible and can be used to add color and flavor to salads and other dishes. The petals can also be dried and used to make tea. In terms of medicinal uses, the plant has been used for centuries to treat a variety of ailments, including wounds, infections, and skin irritation. The pot marigold is also attractive to a variety of pollinators, making it a valuable plant for attracting beneficial insects to the garden. Overall, the pot marigold is a versatile and easy-to-grow plant that is well-suited to a variety of garden settings. ### Propagation - Direct sow Direct sow in spring when light frost is still possible. Can be sown until early summer for fall blooms. ### Propagation - Transplant Sow indoors in late winter, transplant outside when risk of heavy frost has passed. #### Links [Calendula @ West Coast Seeds](https://www.westcoastseeds.com/products/zeolights-organic) |
Show
Edit |

|
Chamomile |
5-9
Full sun
Dry, Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
0.5
0.05
Annual
Herbs
at last frost date
1 week
Matricaria recutita - L., German chamomile, wild chamomile
Kamille
Asteraceae or Compositae
Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Altay, Austria, Azores, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Buryatiya, Canary Is., Central European Rus, China North-Central, China South-Central, China Southeast, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, East Aegean Is., East European Russia, Egypt, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, India, Iran, Iraq, Irkutsk, Italy, Kazakhstan, Kirgizstan, Korea, Krasnoyarsk, Kriti, Krym, Lebanon-Syria, Manchuria, Mongolia, Morocco, Myanmar, Netherlands, North Caucasus, Northwest European R, Norway, Pakistan, Palestine, Portugal, Romania, Sardegna, Sicilia, Sinai, South European Russi, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Transcaucasus, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Tuva, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, West Himalaya, West Siberia, Xinjiang, Yakutskiya, Yugoslavia
Alabama, Alberta, Arizona, Arkansas, Baleares, Baltic States, Bolivia, British Columbia, California, Colombia, Connecticut, Corse, Costa Rica, Cuba, District of Columbia, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Ethiopia, Great Britain, Greenland, Guatemala, Gulf States, Honduras, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Ireland, Jawa, Juan Fernández Is., Kansas, Kentucky, Magadan, Maine, Mali, Manitoba, Maryland, Massachusetts, Mexico Southeast, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, New Jersey, New South Wales, New York, Newfoundland, Nicaragua, North Dakota, North European Russi, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Ontario, Oregon, Paraguay, Pennsylvania, Peru, Poland, Primorye, Québec, Rhode I., Saskatchewan, South Australia, Tennessee, Texas, Tunisia, Uruguay, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, Wisconsin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matricaria_chamomilla
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:154715-2
Direct sow in autumn or shortly before latest date of frost
Start seeds indoors 6-8 weeks before last frost date
|
Chamomile is a plant native to Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia. It has a small, daisy-like flower with white petals and a yellow center. The leaves are thin and feathery, and the stem is thin and wiry. Chamomile grows to be about 12-24 inches tall and spreads to about 16-20 inches wide. It grows quickly, producing flowers within a few weeks of germination. Chamomile prefers well-drained soil and full sun to partial shade. It is a hardy plant and can tolerate drought and frost. To cultivate chamomile successfully, it is important to keep the soil moist and well-watered, especially during hot weather. Needs light to germinate. The flowers and leaves of chamomile are edible and can be used in a variety of dishes, including teas and salads. The flowers can also be dried and stored for later use. Chamomile has a number of medicinal properties and has been used to treat a variety of conditions, including anxiety, insomnia, and digestive issues. It is also believed to have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. In addition to its medicinal uses, chamomile can also be used as a ground cover or as a companion plant in gardens. It can help to repel pests and improve the health of nearby plants. Chamomile is also valued by bees and other pollinators, making it an important plant for maintaining biodiversity in gardens and agricultural areas. #### Links [Chamomile @ Plants For A Future](https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Matricaria recutita) |
Show
Edit |

|
Nane |
Nana-minze
Afghanistan, Alaska, Albania, Alberta, Algeria, Altay, Amur, Angola, Arizona, Arkansas, Austria, Azores, Baleares, Baltic States, Belarus, Belgium, Botswana, British Columbia, Bulgaria, Buryatiya, California, Cambodia, Canary Is., Cape Provinces, Cape Verde, Central European Rus, Chad, Chatham Is., China North-Central, China South-Central, China Southeast, Chita, Colorado, Connecticut, Corse, Cyprus, Czechoslovakia, Delaware, Denmark, East Aegean Is., East European Russia, Egypt, Ethiopia, Finland, Florida, France, Free State, Føroyar, Georgia, Germany, Great Britain, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Idaho, Illinois, India, Indiana, Inner Mongolia, Iowa, Iran, Iraq, Ireland, Irkutsk, Italy, Japan, Jawa, Kamchatka, Kansas, Kazakhstan, Kentucky, Kenya, Khabarovsk, Kirgizstan, Korea, Krasnoyarsk, Kriti, Krym, Kuril Is., KwaZulu-Natal, Labrador, Laos, Lebanon-Syria, Lesotho, Lesser Sunda Is., Libya, Madeira, Magadan, Maine, Malawi, Malaya, Maluku, Manchuria, Manitoba, Maryland, Massachusetts, Mexico Central, Mexico Northeast, Mexico Northwest, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Mongolia, Montana, Morocco, Myanmar, Namibia, Nebraska, Nepal, Netherlands, Nevada, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New South Wales, New York, New Zealand North, New Zealand South, Newfoundland, North Caucasus, North Dakota, North European Russi, Northern Provinces, Northern Territory, Northwest European R, Northwest Territorie, Norway, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Oklahoma, Ontario, Oregon, Pakistan, Palestine, Pennsylvania, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Primorye, Qinghai, Queensland, Québec, Rhode I., Romania, Rwanda, Sakhalin, Sardegna, Saskatchewan, Saudi Arabia, Sicilia, Sinai, South Australia, South Dakota, South European Russi, Spain, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Sulawesi, Sumatera, Svalbard, Swaziland, Sweden, Switzerland, Tadzhikistan, Tanzania, Tasmania, Tennessee, Texas, Thailand, Tibet, Transcaucasus, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Turkmenistan, Tuva, Uganda, Ukraine, Utah, Uzbekistan, Vermont, Victoria, Vietnam, Virginia, Washington, West Himalaya, West Siberia, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming, Xinjiang, Yakutskiya, Yugoslavia, Yukon, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Alabama, Amsterdam-St.Paul Is, Argentina Northeast, Argentina Northwest, Argentina South, Bangladesh, Bermuda, Bolivia, Brazil South, Caroline Is., Chile Central, Chile North, Chile South, Colombia, Comoros, Costa Rica, Cuba, District of Columbia, Dominican Republic, Eritrea, Falkland Is., Fiji, Galápagos, Gambia, Gilbert Is., Gulf of Guinea Is., Haiti, Hawaii, Juan Fernández Is., Louisiana, Marianas, Mauritania, Mexico Southwest, Mississippi, Niger, Norfolk Is., North Carolina, Oman, Prince Edward I., Puerto Rico, Society Is., South Carolina, St.Helena, Trinidad-Tobago, Tristan da Cunha, Uruguay, Venezuela
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:30016176-2
|
Show
Edit |
|

|
Cucamelon |
Annual
Full sun
Vines
Seed - direct sow, Seed - transplant
1 week after last frost
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melothria_scabra
Cucamelon, Mexikanische mini-gurke
60-70
23cm, 60cm
6.5-7.0
15-30°c (60-85°f)
Mouse melon
Cucurbitaceae
-3
67
Colombia, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico Central, Mexico Northeast, Mexico Northwest, Mexico Southeast, Mexico Southwest, Nicaragua, Panamá, Venezuela
3-4 weeks before last frost
At last frost
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:293320-1
|
Corn, Sunflowers and any other high growing plant, can act as a trellis. #### Propagation Direct sow when soil temperatures reach 15°C (60°F). Plant inside 3-4 weeks before planting outside, and use bottom-heat to help germination. Transplant when plant develop their third true leaf. #### Links [Cucamelon @ West Coast Seeds](https://www.westcoastseeds.com/products/cucamelon) |
Show
Edit |

|
Leek |
5-9
Full sun
Moist
Light (sandy), Medium
0.9
Herbs
Pest control, Repels carrot rust flies
Bulb, Flowers, Leaves, Root
Seed - transplant
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leek
Garden leek
Alliaceae, Liliaceae
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Allium porrum
sow indoors in containers from Feb., transplant early summer
15cm
Feb. - April
6.0-6.5
< 65°F
Albania, Algeria, Baleares, Bulgaria, Cyprus, East Aegean Is., Egypt, Ethiopia, France, Greece, Iran, Iraq, Italy, Kriti, Lebanon-Syria, Libya, Morocco, Palestine, Portugal, Romania, Sardegna, Sicilia, Sinai, Spain, Transcaucasus, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkey-in-Europe, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Yugoslavia
Alabama, Argentina Northeast, Azores, Baltic States, Belarus, California, Canary Is., Central European Rus, Cuba, Czechoslovakia, Dominican Republic, East European Russia, Galápagos, Great Britain, Haiti, Illinois, Ireland, Kentucky, Madeira, Mexico Central, Mexico Northeast, Mexico Northwest, Mexico Southeast, Mexico Southwest, New South Wales, New York, North European Russi, Northwest European R, Pakistan, Puerto Rico, South Australia, South European Russi, Tasmania, Tennessee, Texas, Ukraine, Victoria, Western Australia
Allium ampeloprasum
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:332079-2
May - July
0.15
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:528646-1
|
The leek is a member of the onion family. It is native to the eastern Mediterranean and parts of Asia. The plant has long, flat, glossy leaves that are typically green in color. It has a white stem that widens into a bulb at the bottom. The plant has a distinctive, onion-like aroma and flavor. Leek plants grow to a height of around one to two feet and have a spread of six to eight inches. They grow relatively slowly, taking around three to four months to reach maturity. Leeks can be distinguished from other members of the onion family by their larger size and more elongated shape. Leek plants prefer moist, well-drained soil and full sun. They can be grown in a variety of soil types but prefer a slightly alkaline pH. To cultivate leeks successfully, a grower should plant them in trenches or hills and keep the soil moist throughout the growing season. Leeks are winter hardy and can be grown in most climates. Usually sown in containers or seed beds first and then moved to their final place a few months later. Leeks are edible and can be used in a variety of dishes. The edible parts of the plant are the white stem and the tender inner leaves. Leeks can be stored in the refrigerator for several weeks after harvest. In addition to their use in cooking, leeks have a number of other uses. They can be used medicinally to treat a variety of conditions, including coughs and respiratory problems. |
Show
Edit |

|
Rocket |
6-9
Annual
Full sun, Partial sun/shade
Dry, Moist
Light (sandy), Medium, Heavy (clay)
0.6
Flowers, Leaves
Seed - direct sow, Seed - transplant
Fast
Brassicaceae or Cruciferae
Oil
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Eruca vesicaria sativa
in spring
25°C
1-3 days
start indoors in pots at a depth
Arugula
Rucola
0.3
|
Rocket, also known as Eruca vesicaria sativa, is a plant native to the Mediterranean region. It is a small, annual plant that typically grows to be about 20-30 cm tall. It has long, narrow leaves that are a pale green color, and small white or yellow flowers. The plant grows quickly and can be differentiated from similar plants by its unique leaf shape. Leaves can be harvested after 3-6 weeks. Rocket prefers to grow in well-drained soil in full sun or partial shade. It likes to grow along tracks, on waste grounds or stony places. To cultivate it successfully, a grower will need to ensure that the soil is moist but not waterlogged, and will also need to protect the plant from extreme temperatures, especially frost. Rocket is not particularly winter hardy, so it may need to be grown in a greenhouse or indoors in colder climates. Rocket is edible, and both the leaves and the seeds can be eaten. The leaves have a spicy, peppery flavor and can be used in salads or cooked dishes. The seeds ripen from July to September and can be roasted and used as a flavoring for dishes or as a garnish. After harvest, the leaves can be stored in the refrigerator for a few days, while the seeds can be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry place for several months. Rocket has several uses beyond its edible parts. It has been used medicinally as a digestive aid and to treat respiratory problems. Rocket is also valuable for wildlife, as it provides food and shelter for a variety of species. Its flowers attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies, and its seeds are a source of food for birds |
Show
Edit |